Privacy Risks from Data Collection
Lesson Objective 2.A: Describe the risks to privacy from collecting and storing personal data on a computer system.
What is Personal Data? (IOC-2.A.1)
Personal data refers to information related to an individual that can be used to identify them, such as:
- Names
- Addresses
- Phone numbers
- Email addresses
- Financial details
- Location
- Browsing history
How and When is Your Data Collected?
- Social media posts
- Creating an account on a website
- Buying an item
- Clicking on a link
- Making a Google search
- Inputting information anywhere

Your data is collected whenever you visit a website for purposes such as security, marketing, or analytics. This information is called PII (Personally Identifiable Information). PII helps sites like Google create a personalized searching experience for you based on data such as:
- Age
- Gender
- Location
- Past search history
While PII offers many benefits, it can also be manipulated, leading to potential privacy risks.
Risks of Collecting Personal Data
- Unauthorized Access: Hackers may gain access to personal data through security breaches, leading to identity theft or financial fraud.
- Data Breaches: Poorly secured personal data can be leaked or stolen, impacting individuals and businesses.
- Misuse of Data: Companies may misuse personal data, such as selling it without consent.
- Insider Threats: Employees might intentionally or unintentionally misuse data.
- Loss of Privacy: Excessive data collection can lead to increased surveillance.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals may use personal data to craft convincing scams.
- Data Persistence: Stored data can be difficult to delete, posing long-term risks.
- Identity Theft: Criminals can use personal data to impersonate someone.
How Can I Prevent This?
- Encryption: Secure data by encrypting stored and transmitted information.
- Strong Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Minimization: Collect and store only the necessary data.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep systems updated to avoid vulnerabilities.
- Access Control: Limit access to personal data based on roles.
- Unique Passwords: Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Compliance with Regulations: Follow laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA for responsible data handling.
🎯 Popcorn Hack: Identify PII
Which of the following is considered PII?
- A. Fingerprint
- B. Favorite Color
- C. Zip Code
- D. Job Title
Safe Computing - B
Safe computing from Collegeboard's AP CSP curriculum
Key Topic - IOC-2.B
Explain how computing resources can be protected and misused.
Authentication Measures - IOC-2.B.1
Authentication measures protect devices and information from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires users to verify their identity using multiple authentication factors.
- Example: Logging into an account with a password and a code sent to a mobile device.
Strong Passwords - IOC-2.B.2
A strong password is easy for the user to remember but difficult for others to guess.
- Example: Q3!xT@9$z is a strong password, while John123 is weak because it can be easily guessed.
- Use at least 8 characters whenever possible.
- Create a passphrase using 4-7 random words.
- Use different passwords for different websites and accounts to prevent one breach from compromising all accounts.
Multifactor Authentication & Security Layers - IOC-2.B.3 & IOC-2.B.4
Multifactor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide multiple pieces of evidence to verify their identity.
- Knowledge (something you know): Example: A password used to log into an account.
- Possession (something you have): Example: A verification code sent to a mobile phone.
- Inherence (something you are): Example: Biometric authentication like fingerprint or facial recognition.
- Why MFA is important: Even if one authentication factor is compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented.
🎯 Pop Quiz: Multifactor Authentication
Which of the following is NOT an example of a multifactor authentication (MFA) factor?
- A. A password used to log into an email account.
- B. A verification code sent to a user's phone.
- C. A fingerprint scan on a smartphone.
- D. A username required to log in.
Answer: (Usernames are identifiers, not authentication factors.)
Encryption - IOC-2.B.5
Encryption encodes data to prevent unauthorized access, while decryption restores it to a readable format.
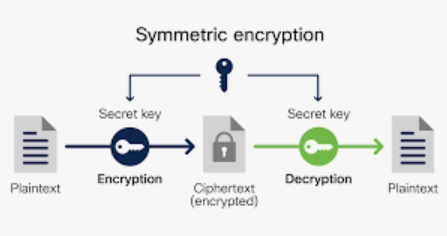
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption.
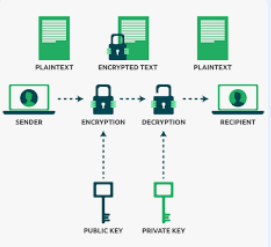
- Public Key Encryption: Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
🔒 Popcorn Hack: Encryption Quiz
- Popcorn Hack (MC question from College Board)
- Which of the following is an example of symmetric encryption?
- A. Evy buys a locked box that operates using two different codes. When the first code is entered, a slot opens that allows a message to be put in the box. When the second code is entered, the door to the box opens. Evy gives the first code to her friends so they can leave messages for her and keeps the second code to herself so that she is the only one who can retrieve the messages.
- B. Finn and Gwen develop a system that maps each letter of the alphabet to a unique symbol using a secret key. Finn uses the key to write a message to Gwen where each letter is replaced with the corresponding symbol. Gwen uses the key to map each symbol back to the original letter.
- C. Hannah writes a message to send to Isabel and hides the message under a rock behind the soccer field. Hannah gives Isabel the exact location of the rock so that only Isabel can find the message.
- D. Juan writes a message to send to Kelly and slides the message through a slot in the front of Kelly’s locker. Juan knows that Kelly has not shared her locker combination with anyone, so no one other than Kelly will be able to read the message.
Certificate Authorities - IOC-2.B.6
Certificate authorities (CAs) are trusted entities that issue digital certificates to verify the authenticity of websites and enable secure encrypted communications.
One widely used tool for obtaining and managing certificates is Certbot, an open-source client developed by the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF).
- Certbot automates the process of obtaining, installing, and renewing SSL/TLS certificates from Let’s Encrypt.
- It simplifies the setup of HTTPS by handling domain validation and configuring web servers like Apache and Nginx.
- Certbot helps website owners maintain security by automatically renewing certificates before they expire, reducing the risk of downtime or security lapses.
- Its user-friendly command-line interface makes it accessible for both beginners and experienced administrators.
Antivirus and Malware Protection - IOC-2.B.7
Antivirus software detects, prevents, and removes malicious programs from computing systems.
- Uses signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and real-time monitoring to identify threats.
- Blocks suspicious activity, quarantines infected files, and prevents malware execution.
- Best Practices: Keep antivirus software updated, enable real-time protection, and avoid unknown downloads.
Privacy and Permissions - IOC-2.B.11
Users should control the permissions that applications have to protect their privacy.
- Review the permission settings of apps before granting access to personal data.
- Be cautious of apps requesting unnecessary permissions (e.g., a flashlight app asking for microphone access).
- Limit access to the camera, microphone, and location services when not needed.
Safe Computing - C
Safe computing from Collegeboard's AP CSP curriculum
Key Topic - IOC-2.C
Explain how unauthorized access to computing resources is gained.
Phishing - IOC-2.C.1
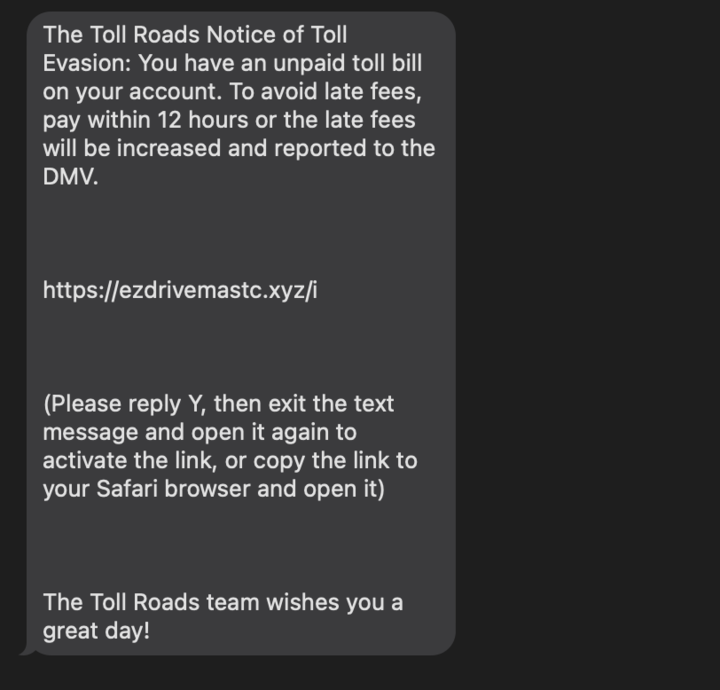
Phishing is a technique that attempts to trick a user into providing personal information. That personal information can then be used to access sensitive online resources, such as bank accounts and emails.
- A lot of you have seen phishing before
- Common examples are email phishing or mobile phishing
- Below is a real example of mobile phishing that Jacob received
- Prevention: Don't click on links from people you don't know or don't trust
Keylogging - IOC-2.C.2
Keylogging is the use of a program to record every keystroke made by a computer user in order to gain fraudulent access to passwords and other confidential information.
- Keylogging does have a few benefits: parental controls or employee monitoring in a business setting
- Other than that, keylogging almost always happens when you install malware
- An application will record your keystrokes
- If you type in a password and username, it would be logged
- Prevention: Don't install untrusted software or apps
Data Interception - IOC-2.C.3
Data sent over public networks can be intercepted, analyzed, and modified. One way that this can happen is through a rogue access point.
- Examples of this can be seen when people set-up fake wifi networks and capture all data being transferred to it or DNS spoofing, which is when an attacker sends you to a unintended IP address after they hijack a DNS server.
- Prevention: Connect to secure networks and verify the address of websites you connect to are legitimate.
Rogue Access Point - IOC-2.C.3
A rogue access point is a wireless access point that gives unauthorized access to secure networks.
- This is part of data interception.
- It is when a access point is installed on a network without owner knowledge or permission.
- Passive interception: reads data but cannot manipulate
- Active interception: can read and manipulate data
- Prevention: Connect to trusted networks and only send information via websites with HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), to ensure data is encrypted.
Malicious Links - IOC-2.C.5
A malicious link can be disguised on a web page or in an email message.
- These are links that send you to illegitimate websites or links that send you to a malware download.
- Seen in many places; websites, ads, emails, texts, etc.
- Prevention: Don't click links that you don't know.
Malicious Emails - IOC-2.C.6
Unsolicited emails, attachments, links, and forms in emails can be used to compromise the security of a computing system. These can come from unknown senders or from known senders whose security has been compromised.
- These emails can contain scams or malicious downloads/attachments.
- After downloading an these attachments, most of them send malicious emails from your account to other people you know
- Therefore, these emails can come from people you know
- Prevention: Don't download files or click random links from emails. If you have to, make sure its someone you know and can verify if it was actually them.
Freeware - IOC-2.C.7
Untrustworthy (often free) downloads from freeware or shareware sites can contain malware.
- Freeware is software that is free to install. Shareware is software where you get a free trial and are asked to pay later.
- Freeware and shareware aren't always malware, but a lot is
- Prevention: Don't download software for free, especially if there is a popular paid version. If you have to, make sure it's from a trusted site that you know and can verify has no malware.
Real Life Example
You connect to an unsecure free wifi at a coffee shop. You send private information on an unsecure http website (NOT https). What you don't know is that someone set up a rogue access point in the shop. They named their fake wifi "WiFi Coffee Shop Free" while the real WiFi was "Free Coffee Shop WiFi." They can read and even manipulate the packets you send via the network before they relay it to the real network. Or they can send you to a different website than the one you intended to go to, possibly injecting malware or stealing info.
🔑 Popcorn Hack: Password Security
Go to security.org/how-secure-is-my-password and make a secure password.
Write and discuss with the people around you about what makes a good password.
Lesson Homework
Answer the multiple choice questions on this Google Form